Publications
Top-Gated Chemical Vapor Deposition Grown Graphene Transistors with Current Saturation
J. Bai, L. Liao, H. Zhou, R. Cheng, L. Liu, Y. Huang, and X. Duan
Nano Lett. 11, 2555-2559 (2011)
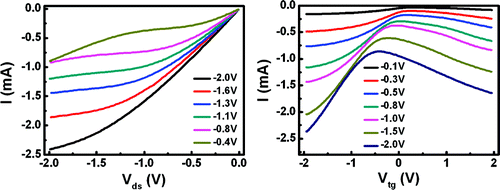
Graphene transistors are of considerable interest for radio frequency (rf) applications. In general, transistors with large transconductance and drain current saturation are desirable for rf performance, which is however nontrivial to achieve in graphene transistors. Here we report high-performance top-gated graphene transistors based on chemical vapor deposition (CVD) grown graphene with large transconductance and drain current saturation. The graphene transistors were fabricated with evaporated high dielectric constant material (HfO2) as the top-gate dielectrics. Length scaling studies of the transistors with channel length from 5.6 μm to 100 nm show that complete current saturation can be achieved in 5.6 μm devices and the saturation characteristics degrade as the channel length shrinks down to the 100–300 nm regime. The drain current saturation was primarily attributed to drain bias induced shift of the Dirac points. With the selective deposition of HfO2 gate dielectrics, we have further demonstrated a simple scheme to realize a 300 nm channel length graphene transistors with self-aligned source–drain electrodes to achieve the highest transconductance of 250 μS/μm reported in CVD graphene to date.
UCLA, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
607 Charles E. Young Drive East, Box 951569
Los Angeles, CA 90095-1569
E-mail: xduan@chem.ucla.edu
607 Charles E. Young Drive East, Box 951569
Los Angeles, CA 90095-1569
E-mail: xduan@chem.ucla.edu







